ACIS® IT Solutions, a managed service provider based in Springfield, MO, offers a comprehensive fiber optic cable repair service. Their team of skilled technicians is trained to diagnose and repair issues with fiber optic cables quickly and efficiently. They use cutting-edge equipment and techniques to ensure that their repairs are of the highest quality and minimize downtime for their clients. ACIS® IT Solutions understands the critical importance of reliable high-speed network connectivity for businesses, so they prioritize providing fast and reliable fiber optic cable repair services. Their experience working with fiber optic cabling has made them a trusted partner for many Springfield, MO businesses seeking top-quality IT solutions. Whether repairing damaged cables or upgrading existing networks, ACIS® IT Solutions provides practical solutions that meet the unique needs of its clients.


Fiber Optic Cable Repair Service

Professional Fiber Optic Network Repair Services
Fiber optic networks have become increasingly critical for businesses worldwide as they offer faster Internet speeds and more reliable connections than traditional copper cables. As a result, companies rely on fiber optics to provide the backbone of their communications systems. To ensure that your business gets the maximum performance out of its fiber optic network equipment and connections, hiring experienced professionals who can perform repairs and maintenance is essential.
ACIS® IT Solutions is one of Springfield, MO’s leading managed service providers, providing comprehensive fiber optic cable repair services. Their team of highly skilled fiber optic technicians has extensive experience in diagnosing and repairing issues with fiber optic cables quickly and effectively. By employing state-of-the-art tools and techniques, they can inspect, clean, service, and repair fiber optic equipment with the utmost precision and efficiency.
Moreover, ACIS® IT Solutions offers certified technicians with specialized industry certifications that attest to their skill levels in performing intricate repairs on fiber optic networks. This gives customers peace of mind knowing that their fiber optic network is serviced by experts who have undergone rigorous training. As a result, any issue is resolved promptly without compromising performance.
When you rely on ACIS® IT Solutions’ expertise for your fiber optic cable repair needs, you can rest assured knowing you’re getting the highest quality repairs. With their fast response times and friendly customer service staff always ready to answer any questions, there’s no better way to ensure optimal performance from your business’s communication system than entrusting it in the hands of ACIS® IT Solutions’ dedicated team of professionals.
Broken Fiber Optic Cables
Broken fiber optic cable can lead to data transmission issues. Fortunately, the problem can be resolved by repairing the cable.
If the damage is minor, it can be repaired by splicing together a broken cable section. This is more cost-effective than having to replace the entire cable.
Fiber optic cable can be damaged due to construction work or weather conditions. If damage occurs, it could affect your company’s network access, so it is essential to act quickly.
The glass core of the fiber optic cable is delicate and can easily break if pulled or unspooled under excessive tension. Additionally, the core can crack when bent at an acute angle.
Fortunately, most broken or damaged cable can be repaired rather than replaced. A technician typically uses a fiber optic cutter, cuts out the damaged section of the cable, and then splices it back together to restore it to working order.
Once a broken or damaged fiber optic cable has been identified, it should be removed and repaired by an experienced technician. If the cable isn’t functioning correctly, it may need to be replaced entirely.
Another way to test a fiber optic cable is by passing it through a laser. While this method may not be as accurate as an OTDR test, it will indicate the cable’s condition and whether it can be repaired or needs replacing.
OTDR Tests
Network engineers use optical fiber testers called Optical Time Domain Reflectometers (OTDRs) to diagnose problems with fiber cables and determine their structural soundness. OTDRs use high-power light pulses to transmit signals down a fiber, then measure any light reflected back onto the port. These events, known as “backscattered” or “reflected,” indicate loss in the cable plant if its power has been significantly reduced or it cannot travel the total distance down its fiber.
An optical depth sounder (OTDR) used to inspect a cable’s length can detect incorrectly installed bends, breaks, and high-loss splices. It can also detect kinking and tight bend radius issues caused during installation – leading to one end of the cable being significantly shorter than its other ends.
Ghosts, Gainers, and Reflective Attenuation
Ghosts on an OTDR trace are caused by highly reflective events in the link under test. While they may seem scary, technicians can quickly identify and eliminate an OTDR ghost by cleaning or replacing the connector. They may also use index matching gel to reduce ghosts on the trace further.
Gainers are a similar phenomenon occurring when light is reflected from one substance to another with an index of refraction different than that of the glass it passes through. For instance, they can occur when light leaves the core of a fiber and encounters either an air gap within a connector or pass through an index-matching gel in a mechanical splice.
Reflective events often appear as a spike before attenuation, typically indicating a connector or mechanical splice in the line.
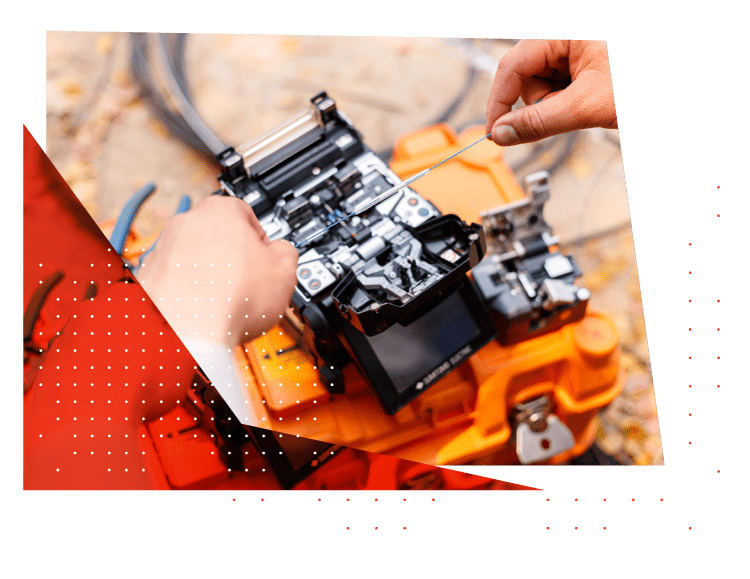

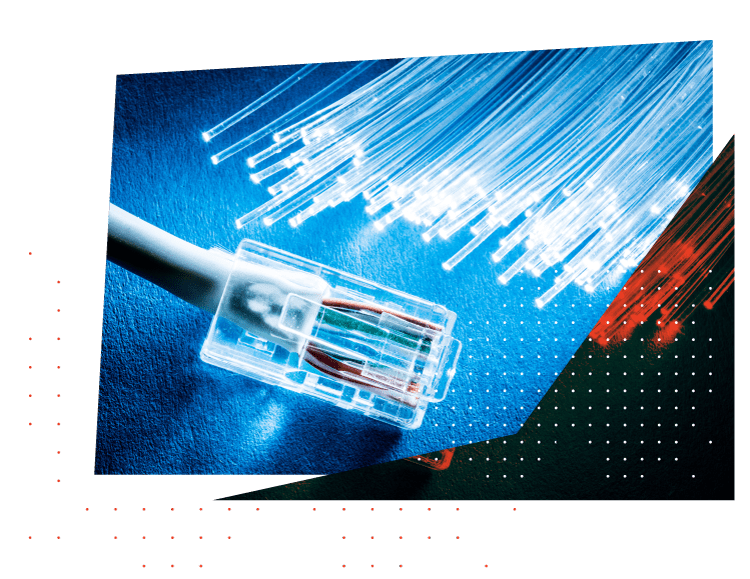
Fiber Optic Splicing
Splicing is a widely used technique for connecting two or more fibers. It’s beneficial when the cable runs are too long for one length of fiber, when repairing severed underground cables, or rejoining broken ones after accidental damage.
Splicing fiber can be done via various methods, such as mechanical splicing and fusion splicing. Each has advantages and drawbacks, so you should decide which option best meets your requirements.
Before splicing, the first step is to use a fiber optic stripper to strip away protective coatings, jackets, tubes, strength members, and other materials from both ends of the fiber. Doing this helps guarantee its integrity during splicing and increases its success rate.
Next, use a fiber cleaver to trim any irregularities at the fiber end and create an exact break, thus reducing signal loss. Cleaving as close to the center is best for the best results.
Once the cleave is complete, both ends are inserted into a fusion splicer.
Replacement
Replacing broken fiber optic cable is a complex process, requiring specialized tools and knowledge. However, with the help of ACIS® IT Solutions’ experienced technicians, this task can be completed quickly and efficiently. The team’s technicians will inspect the cable in question to determine which sections need to be replaced. Then, they will use specialized splicing machines to join the two cable lines together. To ensure the connection is reliable and secure, technicians will inspect for any weak spots and test for abnormalities.
In addition to replacing broken fibers, ACIS® IT Solutions also offers a comprehensive fiber optic cabling installation service for businesses looking to upgrade their telecommunications infrastructure. They provide high-grade cables that can support high-speed data transmission at extended distances than traditional copper cables and can reduce the signal loss caused by electromagnetic interference.
Overall, ACIS® IT Solutions provides an efficient solution to repair or replace broken fiber optic cables. Their fiber optic cabling service is reliable, secure, and cost-effective, allowing businesses to maximize efficiency while minimizing downtime due to cable failures or malfunctions.
Emergency Repairs
ACIS® IT Solutions handles emergency repairs to broken fiber optic cables with extreme urgency and expertise. Their team of experienced technicians has the necessary tools and know-how to troubleshoot and fix any issue as quickly as possible. They understand how critical it is for businesses to have reliable access to their data, so they prioritize emergencies over non-critical ones. The technicians also use sophisticated testing equipment to ensure the repaired cable meets or exceeds industry standards. When a cable is too damaged to be repaired, they offer replacement options that work best for the customer’s budget and needs. ACIS® IT Solutions provides reliable service every time, ensuring your fiber optic cable remains in top condition all year round.
Contact ACIS® IT Solutions for All Your Fiber Optic Repair Needs
If your company’s fiber optic cable is damaged or malfunctioning, contact ACIS® IT Solutions for comprehensive repair service. Their experts are trained to diagnose and repair any problem with fiber optics quickly and efficiently. They also provide emergency repairs and installation services to ensure businesses always have access to their data. Rely on ACIS® IT Solutions for all your fiber optic needs and experience the most reliable service in the industry. With their help, you can keep your company’s fiber optics running at peak performance. Contact them today to learn more about their services!


“Our travel agency, The Travel Group, had ACIS® and Travis do our complete system installation in 2000. An excellent installation. Since then ACIS® has maintained and serviced our computers, networks and printers. They do a super job, they are here promptly, diagnose and treat the problem quickly and are available when we need them, We recommend ACIS® without reservation!”
Doc Don